In the last decade, banks in Mainland China have been actively expanding their retail credit businesses. The proliferation of products such as credit cards, auto finance, consumer loans, Internet loans, personal business loans and inclusive micro and small loans has facilitated the expansion of retail loans, resulting in huge profits to the banking industry. However, product homogeneity has intensified the competition in the retail credit business. How can banks stay competitive?
From Risk Management to Risk Engagement
In the traditional operating structure of banks, risk management is often in the middle, compared to the front-end directly engaging with customers and facing competitive pressure. While the front-end has full access to resources, the risk management department is often positioned as a passive participant cooperating with the strategy of the business department, instead of a value creator.
For the risk management to succeed, it needs to go beyond a passive approach, going all out to establish a complete active risk control system. A successful “risk management” strategy is only possible when there is a complete management system linking the pre-loan, in-process and post-loan processes holistically. However, most of what is deemed as “risk management” today remains at a “risk elimination” stage, undermining a greater potential of “risk management” for business growth and customer value realisation.
Today’s businesses need to balance their risk appetites when running their retail credit businesses. The retail credit industry is a mixture of risks and returns, with the ultimate goal of ensuring “risk engagement”. The landscape in China today highlights how the pioneers in retail banking and the Internet finance industry have made a brave attempt in “risk engagement”, creating differentiated portfolios by means of pricing, limit, segment orientation and the like to enhance business efficiency and market competitiveness to balance risk and return.
Although “risks” and “business” are seemingly contradictory, it is precisely the unification of the two that ensures business health from the perspective of the overall interests of a business. What “risk engagement” actually requires is to adopt a holistic management viewpoint, and to maintain the integrity and consistency of the business as a whole from the macro level to the micro level, and from strategic planning to strategy implementation, to identify the best achievable goals and implement the plan through overall coordination.
Marketing Optimisation for Risk Engagement
As a global leader in retail lending consulting and analytics, Experian observes that competition in the retail lending industry is a result of competing priorities in operations and efficiency. One of the key features of the retail banking business is a large customer base and having to cover multiple marketing channels and service portfolios. This means that retail banks need to have the capability to get the right products and services at the right time in front of the right person. Experian Marketing Optimisation is specially designed to help banks identify the best offer and contact opportunity from multiple options for customers.
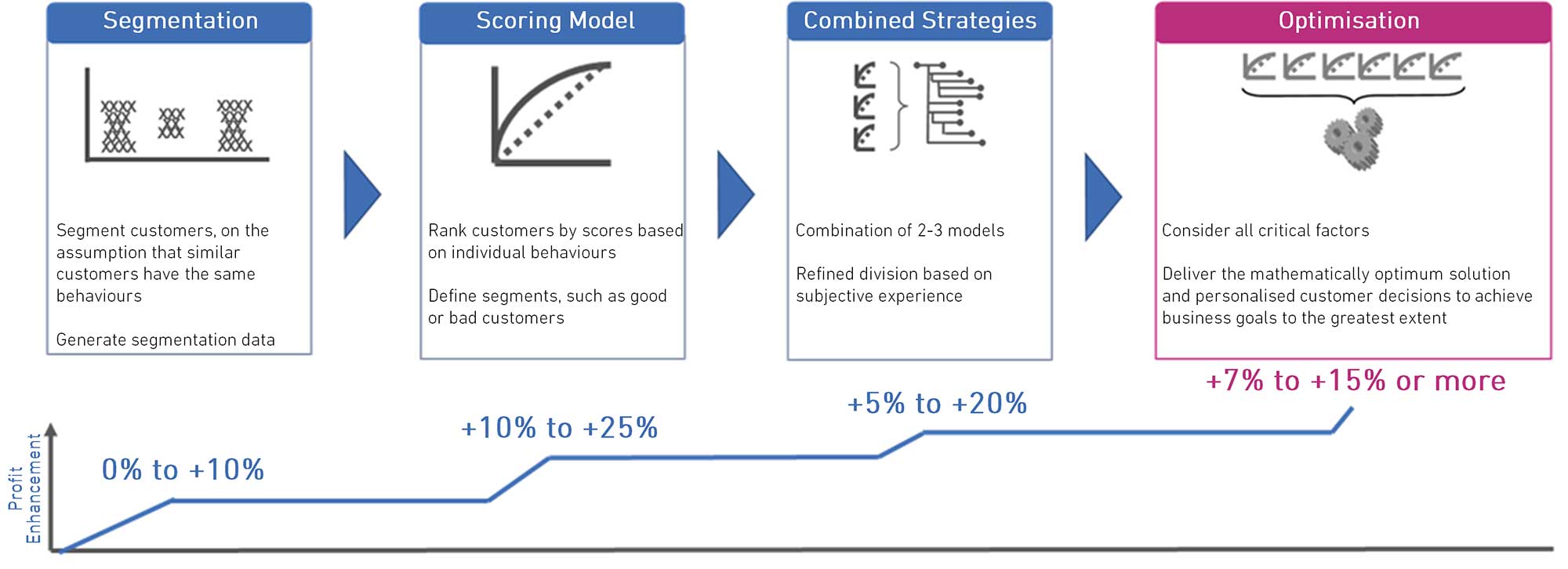
Optimisation is an operational research methodology focusing on achieving critical business goals under established constraints with complex factors taken into consideration. It is widely used in engineering, military, retail and other fields, and highly aligned with the business goals of retail banks. Experian has applied the optimisation methodology to retail banking scenarios, particularly to retail lending and intelligent marketing. The objective is to reap rewards in pricing management, limit management, outbound call management, and other fields, with Experian developing our own three-step strategy:
- Plan critical business goals. While the primary goal of commercial activities is to maximise profit, businesses with different sizes in different business phases may have a different focus. For instance, businesses in the expansion phase may prioritise the increase in revenue or business scale.
- Establish an “action-response” paradigm. This means considering the level of customer acceptance in terms of different management behaviours of banks, such as change in interest rate (price), limit adjustments, difference in marketing channels, and adjustments to risk policies, which may lead to different customer choices and subsequent results. For instance, access to a higher credit card limit may lead to increased overdrafts bringing about increased revenue, but it may also mean excessive debt for customers and result in losses for banks.
- Determine constraints. Constraints include capital limits, local laws and regulations, credit policies limits and others at the macro level, as well as the upper limits of marketing capacity, operational capacity and others at a micro level.
Combining the three aspects above, we are able to construct a utility function, and refine historical data to derive a new business strategy.
Experian’s sophisticated Marketing Optimisation is dedicated to constructing an interior loop that breaks the core goals of businesses down to each C-end user, identifies the best offer and contact opportunity for each of them through personalised algorithms, and the ability for integration. This serves as the best solution for the overall decisioning strategy, so as to maximise the interests of businesses and deliver the best experience to C-end users.
Real Cases of Optimisation
How can we achieve “risk engagement” with Optimisation? Here are two case studies:
Case 1: Implement Optimisation through limit management. Experian Asia Pacific helped a retail bank with five million credit card customers to optimise their credit card limits. With a complete risk management system in place, the retail bank formulated a limit strategy with a complex strategy tree. They questioned whether such a complex limit strategy had provided the best solution for business growth, and whether it could ensure the completion of their “risk management” tasks. Experian Consulting Service redesigned the limit strategy tree with Optimisation model and software, and achieved a 14% increase in profit while reducing the non-performing outstanding balance to a certain extent, without changing the overdraft scale (capital constraints).
Case 2: Implement Optimisation through pricing management. Experian provided a large Chinese bank with a staged pricing consultation service. Having a complete risk management system and a staged business system, the bank could improve the flexibility of its pricing strategies and customer engagement. Experian Consulting Service derived a profit equation to deconstruct the business model, and formulated differentiated pricing strategies with Optimisation model and software in order to provide different customers with targeted offers and contact opportunities for personalised services. This dramatically increased the overall overdraft scale and profit of the business. Meanwhile, the risk indicators showed a slight increase within the controllable scope, achieving the desired result for the bank and attaining their goal of “risk engagement”.
While the application of Optimisation in China is still in the initial stage and developing at a slow pace, it is much easier for most highly developed businesses to construct an Optimisation model from a mathematical perspective in the long term due to the maturity of the methodology. One problem remains: could a perfect Optimisation model stand the test of time in the face of fierce competition and rapid changes in the retail lending market? In response to this challenge, Experian has developed a sophisticated software solution that packages model development and application, as well as a quick response mechanism to enable businesses to quickly be equipped with Optimisation.
Experian Marketswitch® Optimisation is a typical model of commercialising optimisation methodology, which packages the mature model and management system of optimisation and provides a visual interface for business users, helping banks realise fast development and iteration of the optimisation pricing model. Through the graphical interface of Marketswitch® Optimisation, strategy analysts can develop, iterate and quickly deploy the optimisation model, even without any knowledge about modeling.
Experian’s global case studies implementing Marketswitch® Optimisation show that our optimisation service can produce a 7-15% increase in business profit for banks, compared with the conventional model method.
Download our Marketswitch® Optimisation white paper for more insights right now.
